Facts & Origin
What is the origin of a Lhasa Apso?
The Lhasa Apso comes, as the name describes, from Lhasa. Lhasa is the capital of Tibet, an autonomous region in China. The Tibetans bred him already 2000 years ago in noble houses, monasteries and the palace of the Dalai-Lama. In 1901 the first dogs were imported to England and in 1934 they were officially registered and given a breeding standard. In 1970 enthusiasts started breeding in Germany. Lhasa Apsos are listed in the FCI under group nine in section five, in the American Kennel Club (AKC) under the "non-sporting group" and in the British Kennel Club (KC) under the "utility breed group".




| Alternate Name | - |
| Origin | Tibet |
| Life expectancy | 12 - 16 years |
| Care requirements | high-maintenance |
| Activity level | low |
| FCI group | Tibetan breeds |
| AKC group | non-sporting group |
| KC group | utility group |
Lhasa Apso mixes
Attitude, character and temperament of the breed
What are the typical characteristics of a Lhasa Apso?
He is considered a self-confident, cheerful and lively dog that comes across very proud. His sensitive nature is expressed in his constant search for affection and love. Towards his humans he is very affectionate and loving, without giving up his own will. He has a sharp ear, which he uses to announce strangers without barking much. He is initially suspicious of strangers.
Character
Usage


What are typical diseases of Lhasa Apsos?
Their shortened nasal bridge can cause problems in some cases. Sometimes eye diseases, hip joint dysplasia and patella luxations occur as well.
Lhasa Apso breeding - where, how, what?
If you want to give a Lhasa Apso puppy a new home, there are several possibilities. On the one hand, you can turn to a reputable breeder who is affiliated with the VDH. You can find information on the VDH website under the tab "Breeders with puppies". You should make sure that the parents do not have too long fur, which impairs the movement. In addition, they should be tested for typical breed diseases.
On the other hand, it is always worthwhile to have a look at the local animal shelter.
What should be considered when keeping a Lhasa Apsos?
The coat care takes a lot of time. At least twice a week you should brush your dog thoroughly. Training these small dogs is also often underestimated. They have a self-confident personality that needs to be trained with patience and consistency from puppyhood onwards. You must not always give in to its fuzzy cute appearance.
Otherwise, keeping a Lhasa Apsos is trouble-free. You can even take it on the plane with most airlines due to his small size.
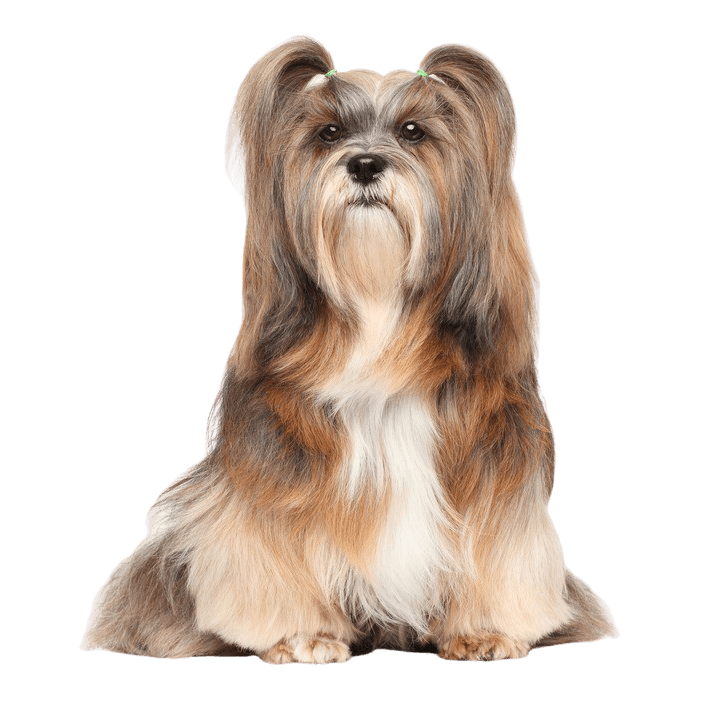


What are the breed characteristics of a Lhasa Apso?
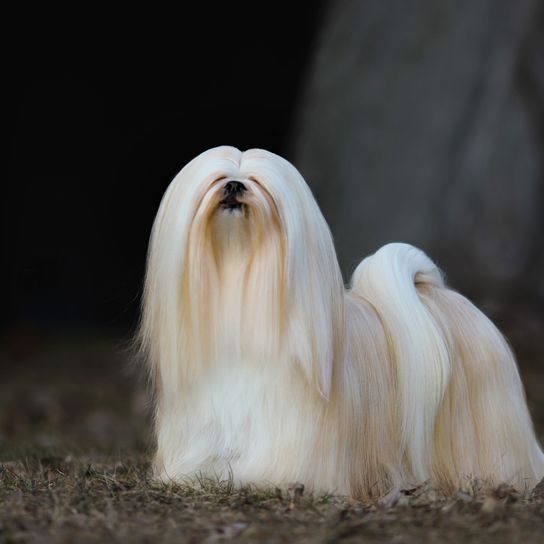
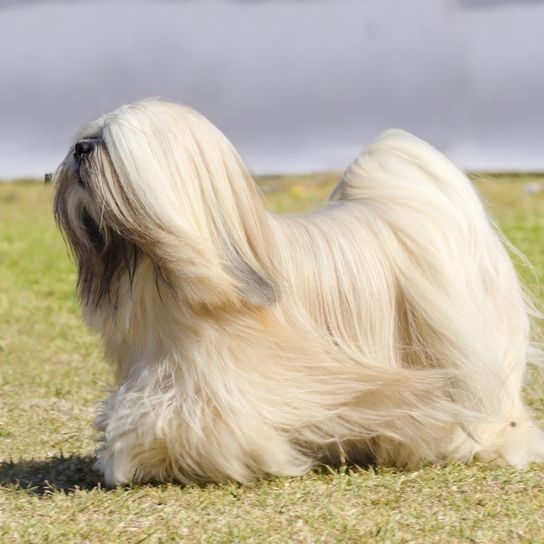
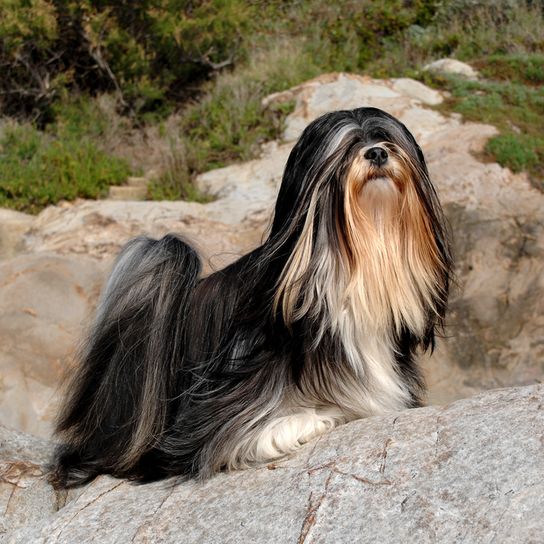
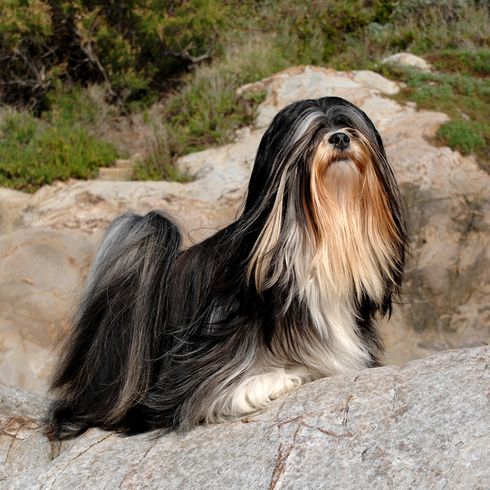
The robust body is well balanced, compact and lushly coated. Its body length is greater than its height. It runs briskly and freely. The head is covered with abundant head hair, but this should not interfere with the eyesight. He has a pronounced beard. The oval eyes are medium sized and dark and the nose is black. Its drooping ears are heavily hairy. The teeth are said to form an inverted scissor in that the upper jaw lies just behind the lower jaw. The high set tail is carried over the back. It often has a kink at the end of the tail and is abundantly hairy.
Appearance and coat of the Lhasa Apsos
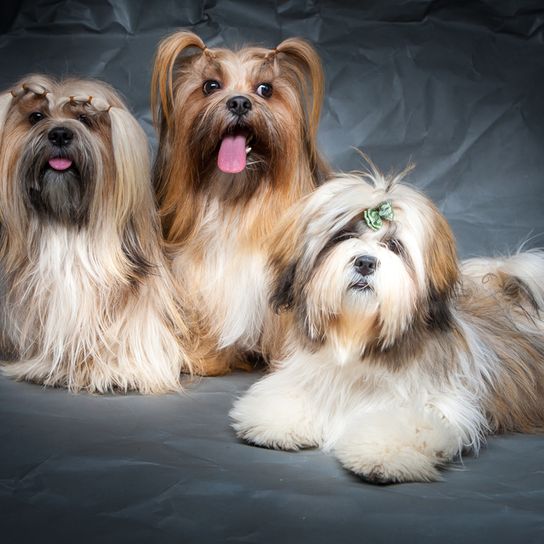
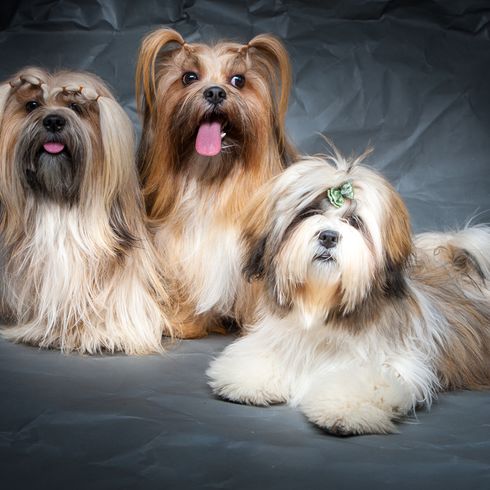
His coat consists of long topcoat, which is straight and heavy. It should never interfere with movement. Under the top coat there is a medium amount of undercoat. The colour palette is varied. The following coat colours are permitted:
- gold
- honey
- slate-coloured
- black
- brown
- white
- smoky grey
- dark-grizzle
- sand-coloured
- bicoloured
How big does the Lhasa Apso become?
The ideal size of an adult male is 25.4 cm. Bitches are slightly smaller.
How much does a Lhasa Apso weigh?
Males weigh six to eight kilograms on average. Bitches weigh five to seven kilograms.
How old does a Lhasa Apso become?
On average, it lives from 12 to 16 years.
| Fur length | long |
| Fur | flat coated |
| Ear shape | Floppy Ear |
| Tail | rolled up |
| Anatomy | slim |
| Size ♀ | 20 - 25 cm |
| Weight ♀ | 5 - 8 kg |
| Size ♂ | 20 - 25 cm |
| Weight ♂ | 6 - 8 kg |
| Suitable For | Beginner, Children, Seniors |
Colors



Known Diseases
Hip dysplasia (HD)
Hip dysplasia (HD) is a genetic condition in dogs where the hip joint is not shaped properly. This leads to pain, stiffness and restricted movement.
Eye diseases
Often occur with allergies and intolerances.
Patellar luxation
Patellar luxation is the term used to describe a displacement of the kneecap, which is one of the most common causes of lameness in dogs.