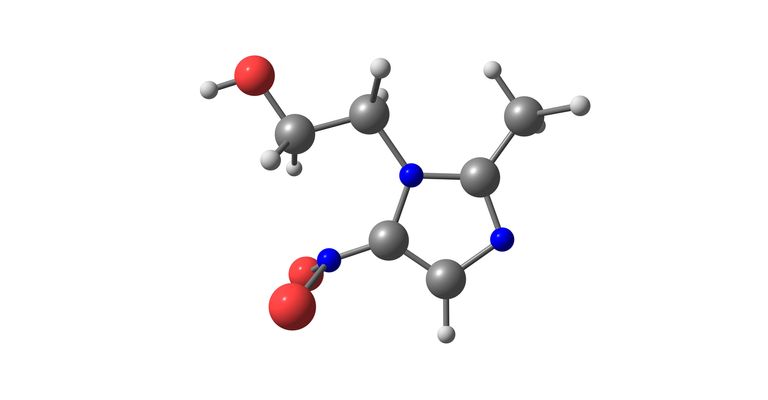
What is Metrobactin?
Metrobactin is an antibiotic for the treatment of certain bacterial infections in dogs (and cats), which achieves rapid results. A veterinarian should always be consulted before use to ensure that there are no undesirable side effects and that treatment is effective.
When is Metrobactin used?
Metrobactin is used for the treatment of infections of the gastrointestinal tract caused by Giardia spp. and Clostridium spp. as well as for the treatment of infections of the urogenital tract, oral cavity, pharynx and skin caused by metronidazole-susceptible anaerobic bacteria (e.g. Clostridium spp.).
However, metronidazole has no clinically relevant effect on facultative anaerobic, obligate aerobic and microaerophilic bacteria.
When should Metrobactin not be used?
As the active substance is primarily metabolized in the liver, particular caution is required in animals with liver damage and the dosage should be adjusted accordingly. In general, Metrobactin should not be used in animals that are sensitive to nitroimidazole derivatives.
Studies in laboratory animals have shown contradictory results with regard to teratogenic (malformation-causing) and embryotoxic effects , which is why use during pregnancy, particularly in the first three weeks of gestation, is not recommended. Metronidazole should also be avoided during lactation as it passes into the milk.
Caution should also be exercised in animals with CNS disorders, as metronidazole may have neurotoxic effects. In such patients, its use can lead to vomiting and aspiration, which is why it should only be used after careful consideration.
Active substance Metronidazole
When metronidazole is taken up by susceptible anaerobic bacteria, it is reduced to metabolites that are toxic to the bacteria by binding to the bacterial DNA. This action usually kills bacteria when the concentration of the active ingredient reaches or slightly exceeds the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is the smallest amount of an antibiotic that stops the growth of bacteria.
Interactions with other medications
If your dog is already taking other medication, it is important that the vet is informed. Metronidazole can inhibit the breakdown of certain drugs (such as phenytoin, cyclosporine and warfarin) in the liver, which can affect their effectiveness.
In addition, cimetidine can slow down the breakdown of metronidazole in the liver, leading to increased serum concentrations. In contrast, phenobarbital can accelerate the breakdown of metronidazole and thus reduce its concentration in the blood.
Administration and dosage
The bioavailability of metronidazole increases when it is administered together with food. However, as the tablets have a very bitter taste , they should not be crushed before administration. It is recommended that metronidazole is used with caution and that patients are carefully monitored, especially when used long-term.
What should I be aware of?
Metronidazole has been shown to have mutagenic and mutagenic properties in laboratory animals and humans. It has been confirmed as a carcinogen in laboratory animals and there is a possibility that it may also be carcinogenic in humans, although there is insufficient evidence. To avoid skin contact, impervious gloves should be worn when handling this veterinary medicinal product.
To prevent accidental ingestion, especially by children, unused portions of the tablets should be returned to the opened cavity of the blister pack and replaced in the box. In the event of accidental ingestion, a doctor should be consulted immediately and the package leaflet or label shown. It is important to wash your hands thoroughly after handling the tablets.
Possible side effects
The following side effects may occur after administration of metronidazole: Vomiting, hepatotoxicity and neutropenia. In rare cases, neurological symptoms may also be observed.
Can Metrobactin cause cancer?
The formation of reactive metabolites occurs through the reduction of metronidazole by both bacterial nitroreductases and reducing enzymes in the mammalian organism. These reactive metabolites are presumably responsible for the mutagenic and carcinogenic effects of the substance.
Conclusion
Metrobactin, a potential dosage form of metronidazole, is an effective agent for the treatment of various bacterial infections in dogs, particularly against anaerobic bacteria. It offers an effective therapeutic option but should be used with caution as it can cause potential side effects such as vomiting, hepatotoxicity and, in rare cases, neurological signs. In addition, special care should be taken in animals with liver or CNS disease and in pregnant or lactating dogs. Careful monitoring and consultation with the vet is essential to ensure the best treatment for the dog.
Sources and relevant links
Emmerich I, Hein J (2018). Dosierungsvorschläge für Arzneimittel bei Kleinnagern, Kaninchen und Frettchen und Igeln. 2., aktualisierte und erweiterte Auflage. Thieme.
Dechra (Metrobactin 250mg)
Accessed on 27.08.2024
Dechra (Metrobactin 500mg)
Accessed on 27.08.2024
CliniPharm/CliniTox
Accessed on 27.08.2024